Introduction to the Linux Operating System
What is Linux?
LINUX is an operating system or a kernel distributed under an open-source license. Its functionality list is quite like UNIX. The kernel is a program at the heart of the Linux operating system that takes care of fundamental stuff, like letting hardware communicate with software.
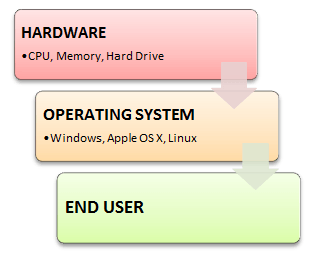
Why do you need an OS?
Every time you switch on your computer, you see a screen where you can perform different activities like write, browse the internet or watch a video. What is it that makes the computer hardware work like that? How does the processor on your computer know that you are asking it to run a mp3 file?
Well, it is the operating system or the kernel which does this work. So, to work on your computer, you need an Operating System(OS). In fact, you are using one as you read this on your computer. Now, you may have used popular OS’s like Windows, Apple OS X, but here we will learn what Linux is and what benefits it offers over other OS choices.
Who created Linux?
Linux is an operating system or a kernel which germinated as an idea in the mind of young and bright Linus Torvalds when he was a computer science student. He used to work on the UNIX OS (proprietary software) and thought that it needed improvements.
However, when his suggestions were rejected by the designers of UNIX, he thought of launching an OS which will be receptive to changes, modifications suggested by its users.
The Lone Kernel & the early days
So Linus devised a Kernel named Linux in 1991. Though he would need programs like File Manager, Document Editors, Audio -Video programs to run on it. Something as you have a cone but no ice-cream on top.
As time passed by, he collaborated with other programmers in places like MIT and applications for Linux started to appear. So around 1991, a working Linux operating system with some applications was officially launched, and this was the start of one of the most loved and open-source OS options available today.
The earlier versions of Linux were not so user-friendly as they were in use by computer programmers and Linus Torvalds never had it in mind to commercialize his product.
This definitely curbed the Linux’s popularity as other commercially oriented Operating System Windows got famous. Nonetheless, the open-source aspect of the Linux operating system made it more robust.
Linux gets its due attention

The main advantage of Linux was that programmers were able to use the Linux Kernel to design their own custom operating systems. With time, a new range of user-friendly OS’s stormed the computer world. Now, Linux is one of the most popular and widely used Kernel, and it is the backbone of popular operating systems like Debian, Knoppix, Ubuntu, and Fedora. Nevertheless, the list does not end here as there are thousands of OS’s based on Linux which offer a variety of functions to the users.
Linux Kernel is normally used in combination of GNU project by Dr. Richard Stallman. All mordern distributions of Linux are actually distributions of Linux/GNU
The benefits of using Linux
Linux now enjoys popularity at its prime, and it’s famous among programmers as well as regular computer users around the world. Its main benefits are –
It offers a free operating system. You do not have to shell hundreds of dollars to get the OS like Windows!
Is it for me?
Users, who are new to Linux, usually shun it by falsely considering it as a difficult and technical OS to operate but, to state the truth, in the last few years Linux operating systems have become a lot more user-friendly than their counterparts like Windows, so trying them is the best way to know whether Linux suits you or not.
There are thousands of Linux based operating systems; most of them offer state-of-the-art security and applications, all of it for free!
This is what Linux is all about, and now we will move on to how to install Linux and which Distribution you should choose.
I am asked to Learn Unix? Then why Linux?
UNIX is called the mother of operating systems which laid out the foundation to Linux. Unix is designed mainly for mainframes and is in enterprises and universities. While Linux is fast becoming a household name for computer users, developers, and server environment. You may have to pay for a Unix kernel while in Linux it is free.
But, the commands used on both the operating systems are usually the same. There is not much difference between UNIX and Linux. Though they might seem different, at the core, they are essentially the same. Since Linux is a clone of UNIX. So learning one is same as learning another.
How to Download & Install Linux (Ubuntu) in Windows
Now that we know what Linux is, it is the time that to learn how we should install it on the computer and choose which Distribution we should use. Let us start by understanding what a Linux Distribution is
What is a Linux Distribution?
Well, now as you know that Linux is open-source, free to use kernel. It is used by programmers, organizations, profit and non-profit companies around the world to create Operating systems to suit their individual requirements.
To prevent hacking attempts, many organizations keep their Linux operating systems private.
Many others make their variations of Linux available publicly so the whole world can benefit at large.
These versions/ types /kinds of Linux operating system are called Distributions.
How many distributions are out there?

There are hundreds of Linux operating systems or Distributions available these days. Many of them are designed with a specific purpose in mind. For example, to run a web server or to run on network switches like routers, modems, etc.
The latest example of one of the most popular smartphone-based Linux Distribution is Android!
Many of these Distributions are built to offer excellent personal computing.
Here, are a few popular Linux Distributions (also called Linux Distro) –
The Best Linux Distribution!
The term best is relative. Each Linux distribution is built for a specific purpose-built to meet the demands of its target users.
The desktop Distributions are available for free on their respective websites. You might want to try them one by one till you get to know which Distribution you like the most. Each one of them offers its own unique design, applications, and security.
We will be using Ubuntu for our learning purpose as it’s easy for a beginner to understand.
Installing Linux
Let’s look the various methods we can use to install Ubuntu.
Installing Linux using USB stick
This is one of the easiest methods of installing Ubuntu or any distribution on your computer. Follow the steps.
steps.

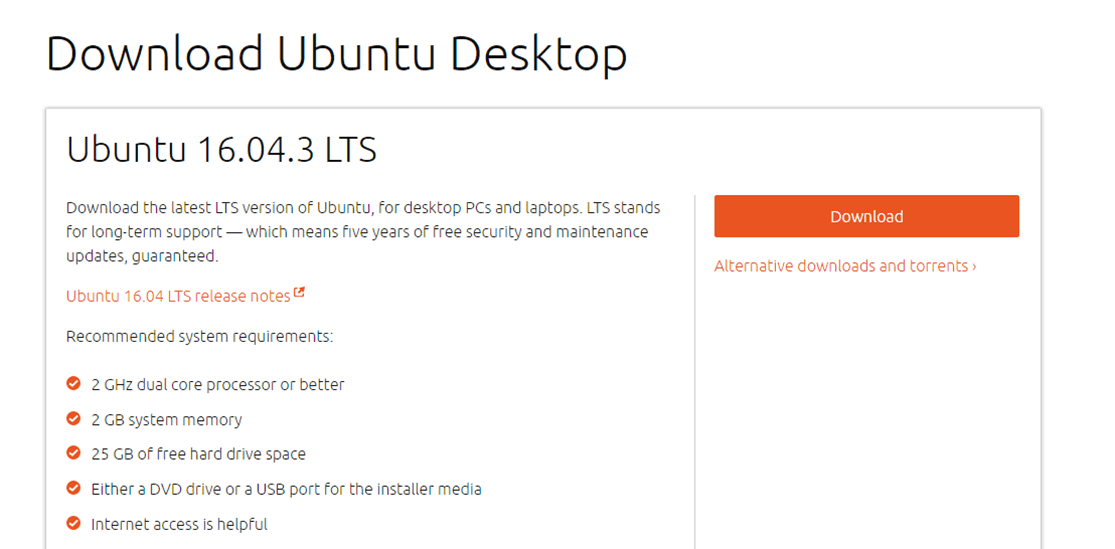
Step 1) Download the .iso or the OS files on your computer from this link.
Step 2) Download free software like ‘Universal USB installer to make a bootable USB stick.
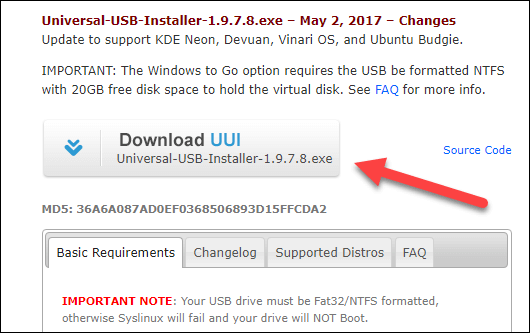
Step 3) Select an Ubuntu Distribution form the dropdown to put on your USB
Select your Ubuntu iso file download in step 1.
Select the drive letter of USB to install Ubuntu and Press create button.
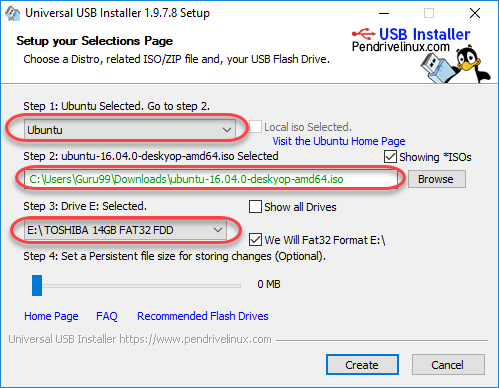
Step 4) Click YES to Install Ubuntu in USB.

Step 5) After everything has been installed and configured, a small window will appear Congratulations! You now have Ubuntu on a USB stick, bootable and ready to go.
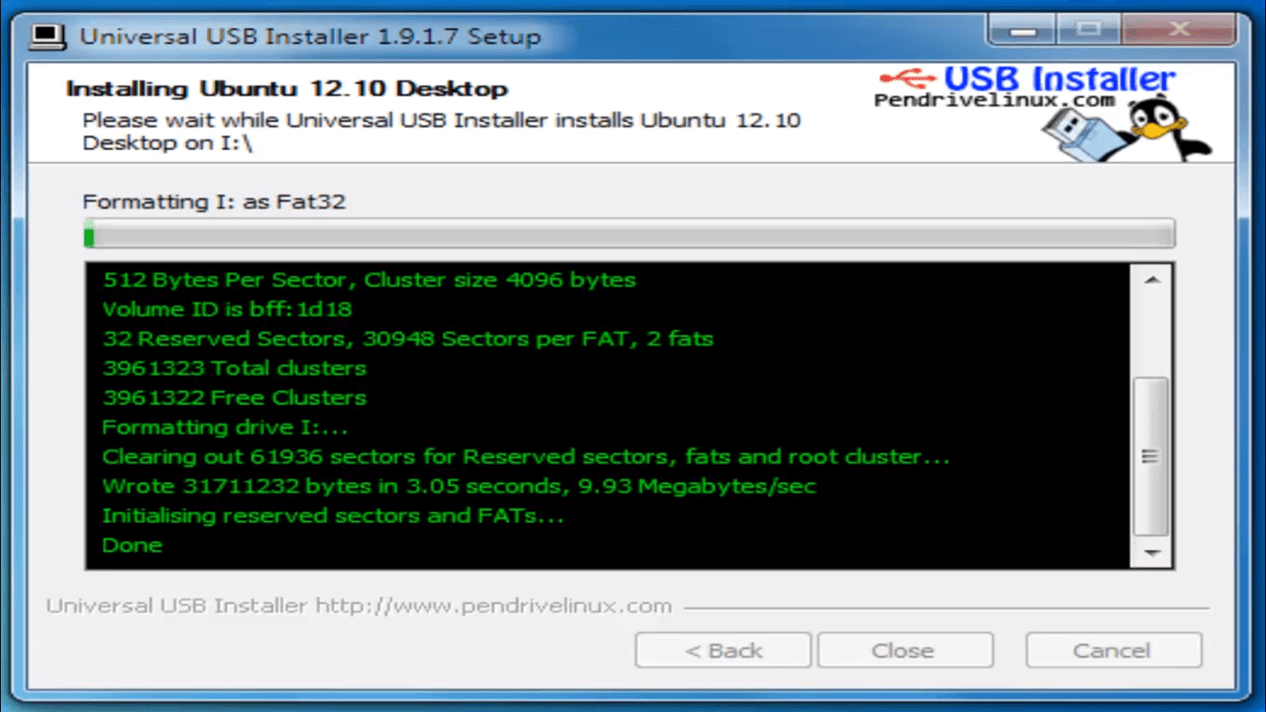
Installing Linux using CD-ROM
Those who like the way a CD runs should try using this method.

Step 1) Download the .iso or the OS files onto your computer from this link
Step 1) Download the .iso or the OS files onto your computer from this link http://www.ubuntu.com/download/desktop.
Step 2) Burn the files to a CD.

Step 3) Boot your computer from the optical drive and follow the instructions as they come.
Installing Linux using Virtual Machine
This is a popular method to install a Linux operating system. The virtual installation offers you the freedom of running Linux on an existing OS already installed on your computer. This means if you have Windows running, then you can just run Linux with a click of a button.
Virtual machine software like Oracle VM can install Ubuntu in easy steps. Let us look at them.
Here the brief steps

PART A) Download and Install Virtual Box
Download Virtual box using this link
Depending on your processor and OS, select the appropriate package. In our case, we have selected Windows with AMD
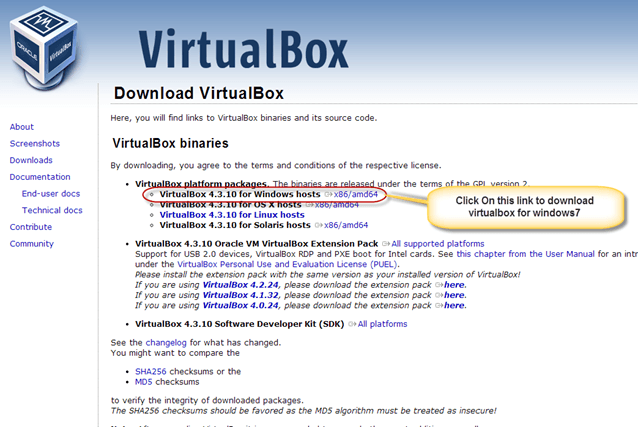
Once the download is complete, Open setup file and follow the steps below:
Step-1) Click On next
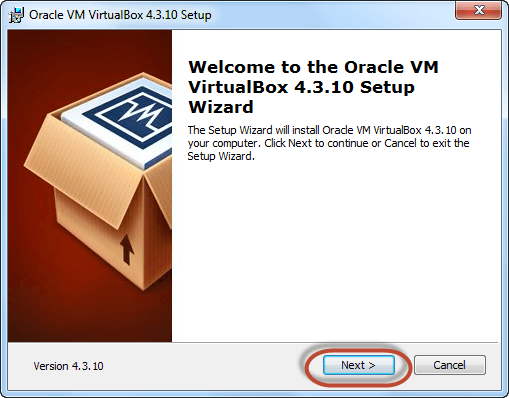
Step-2) Select you’re the directory to install VirtualBox and click on next
Step-3) Select Desktop icon and click on next, now click on yes
Step-4) Click On install.
Step-5) Now installation of the virtual box
will start. Once complete, click on Finish Button to start Virtual Box
The virtual box dashboard looks like this-
PART B) Download Ubuntu
Visit this link to download Ubuntu.
You can select 32/64-bit versions as per your choice.
PART C) Create a Machine in Virtual Box
Step-1) Open Virtual box and click on new button
Step-2) In next window, give the name of your OS which you are installing in virtual box. And select OS like Linux and version as Ubuntu 32 bit. And click on next

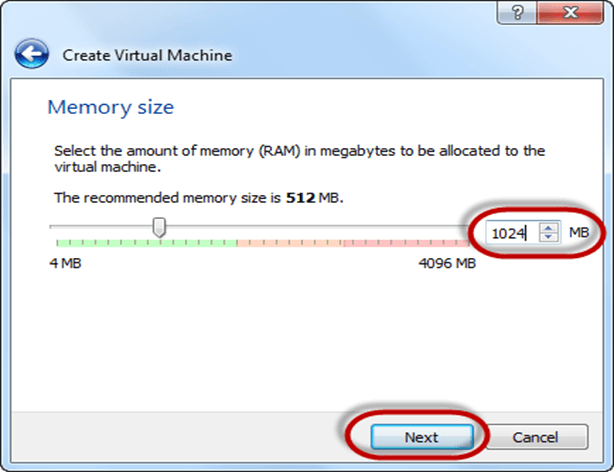
Step-3) Now Allocate Ram Size To your Virtual OS. I recommended keeping 1024mb (1 GB) ram to run Ubuntu better. And click on next.
Step-4) Now To run OS in virtual box we have to create virtual hard disk, click on create a virtual hard drive now and click on create button.
The virtual hard disk is where the OS installation files and data/applications you create/install in this Ubuntu machine will reside
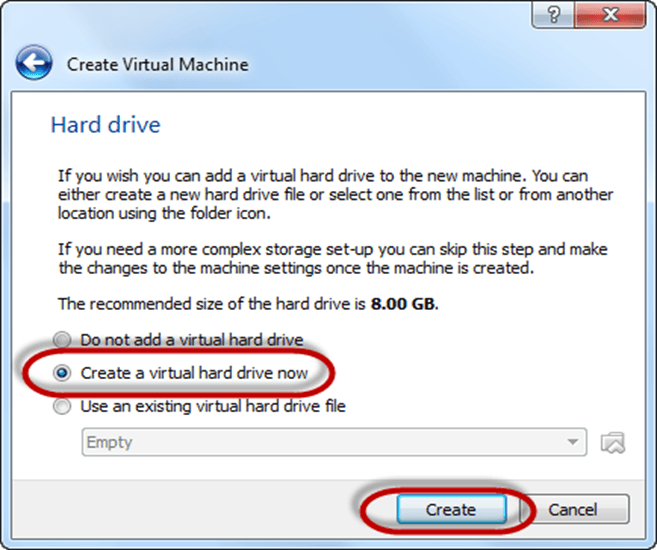
Step-5) select VHD (virtual hard disk) option and click on next.
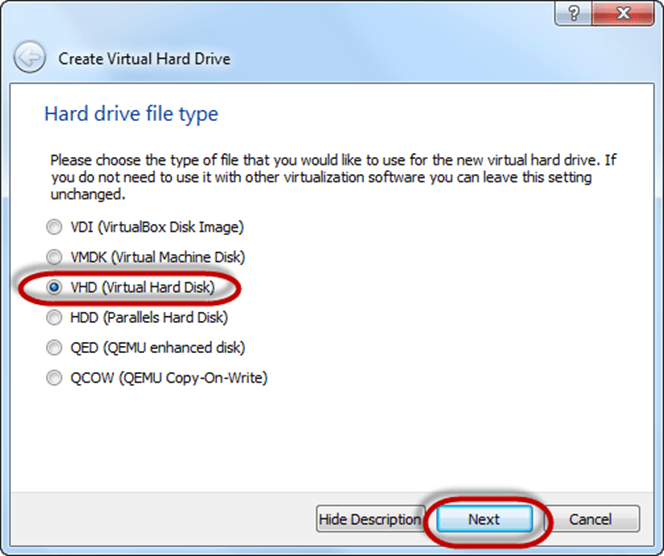
Step-6) Click on dynamic allocated and click on next. This means that the size of the disk will increase dynamically as per requirement.
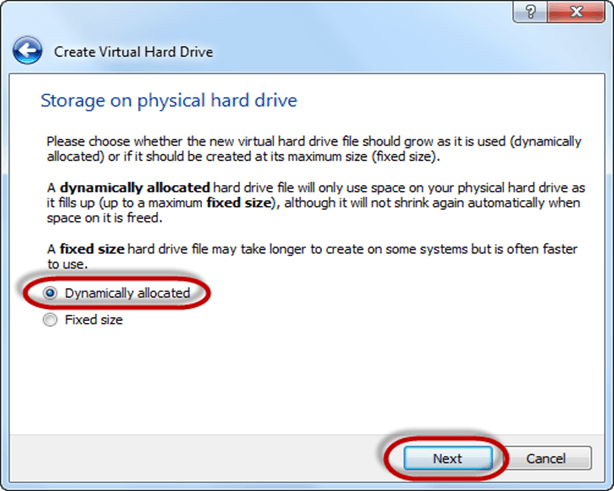
Step-7) Allocate memory to your virtual hard drive .8GB recommended. Click on create button.
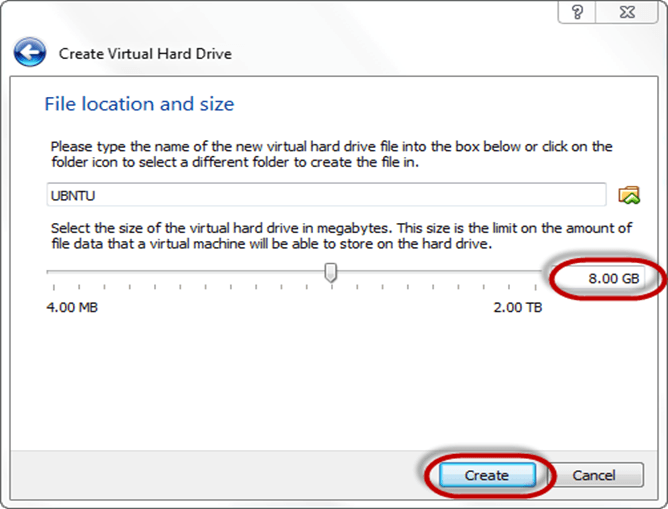
Step-8) Now you can see the machine name in left panel
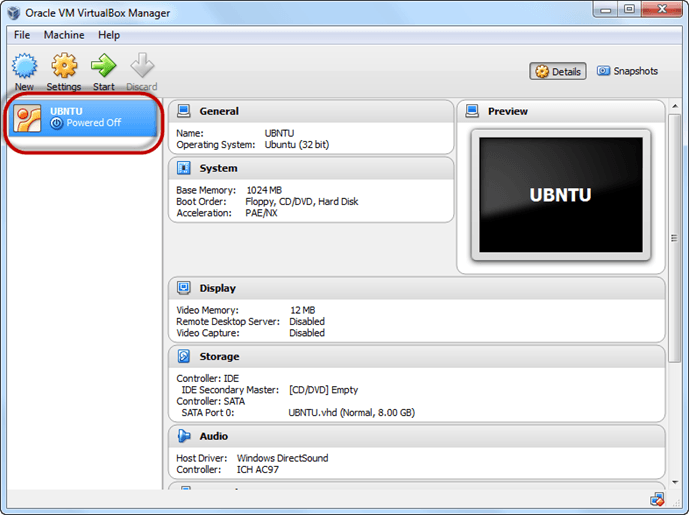
So a Machine (PC) with 8GB Hardisk, 1GB RAM is ready.
PART D) Install Ubuntu on the Machine
Step 1) Select the Machine and Click on Start
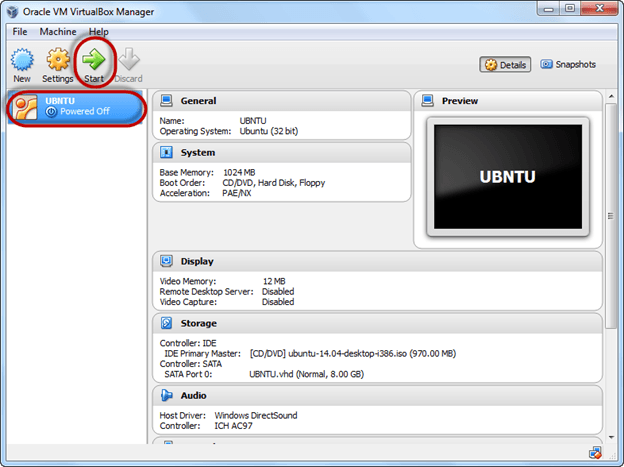
Step 2) Select the Folder Option
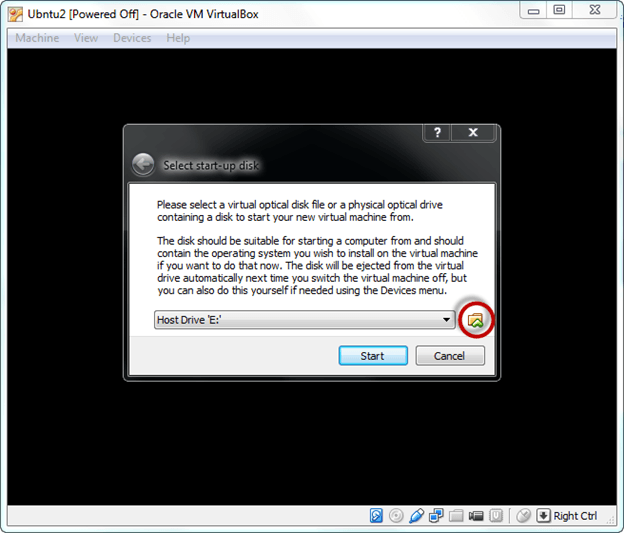
Step 3) Select the Ubuntu iso file
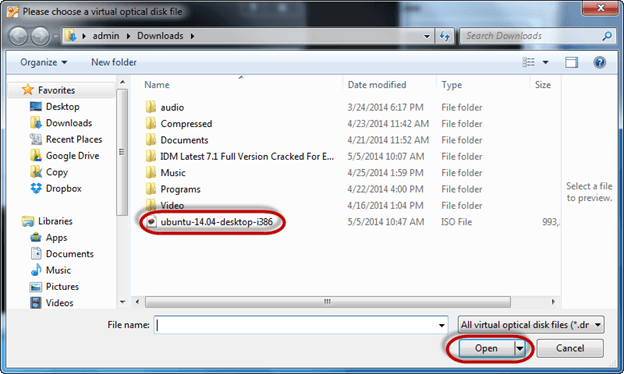
Step 4) Click Start

Step-5) You have an option to Run Ubuntu WITHOUT installing. In this tutorial will install Ubuntu
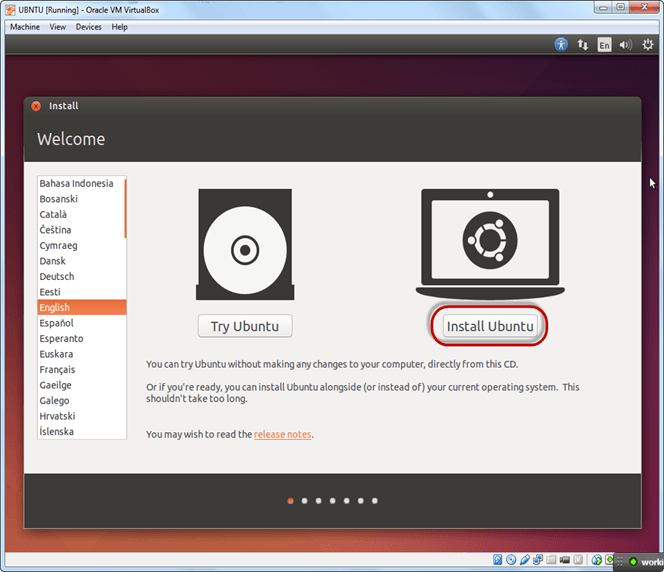
Step-6) Click continue.
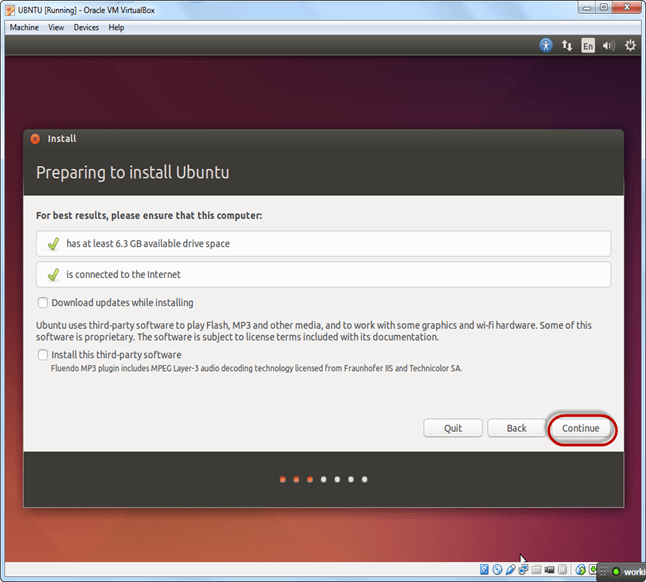
Step-7) Select option to erase the disk and install Ubuntu and click on install now. This option installs Ubuntu into our virtual hard drive which is we made earlier. It will not harm your PC or Windows installation
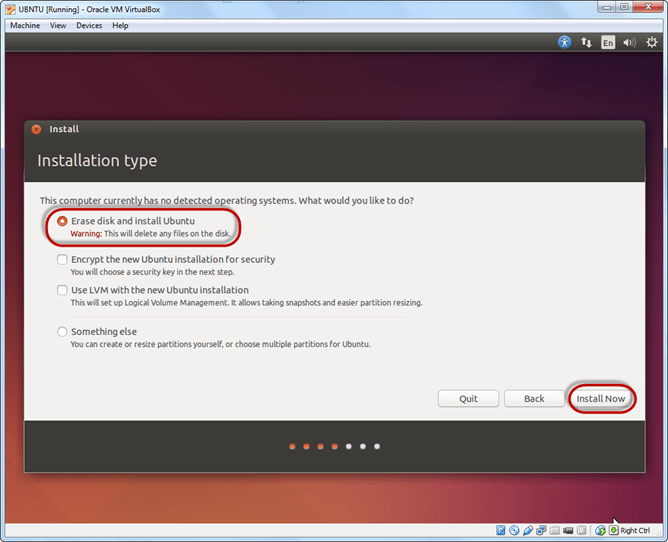
Step-8) Select your location for setting up time zone, and click on continue
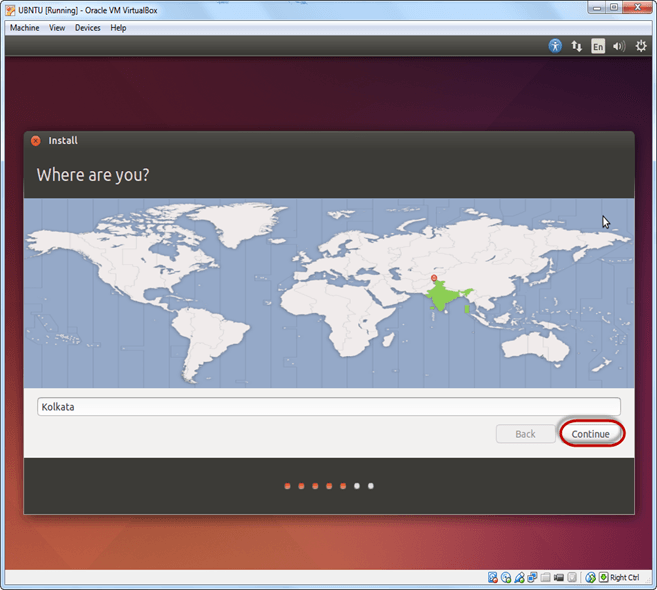
Step-9) Select your keyboard layout, by default English (US) is selected but if you want to change then, you can select in the list. And click on continue
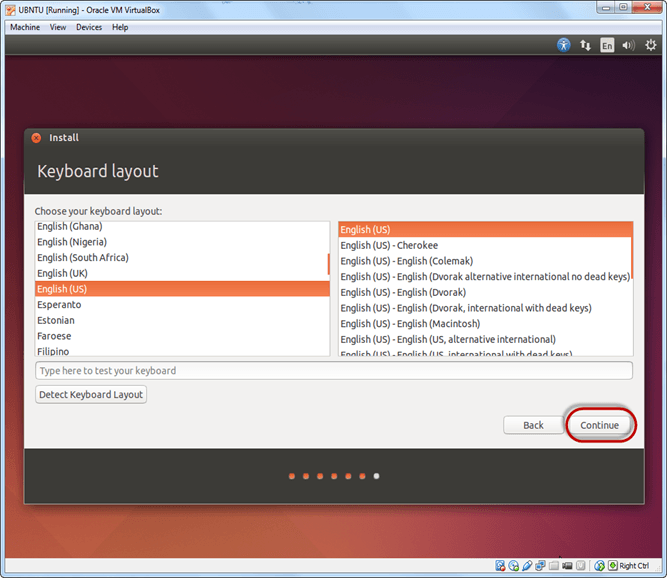
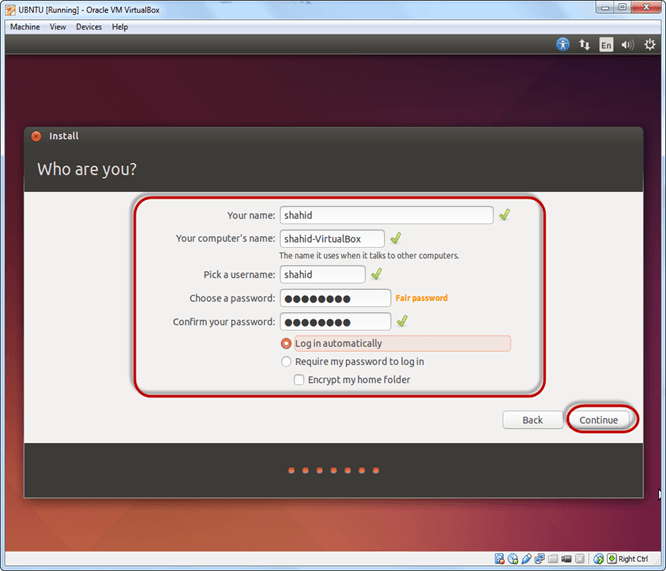
Step-10) Select your username and password for your Ubuntu admin account. This information has been needed for installing any software package into Ubuntu and also for login to your OS. Fill up your details and tick on login automatically to ignore login attempt and click on continue
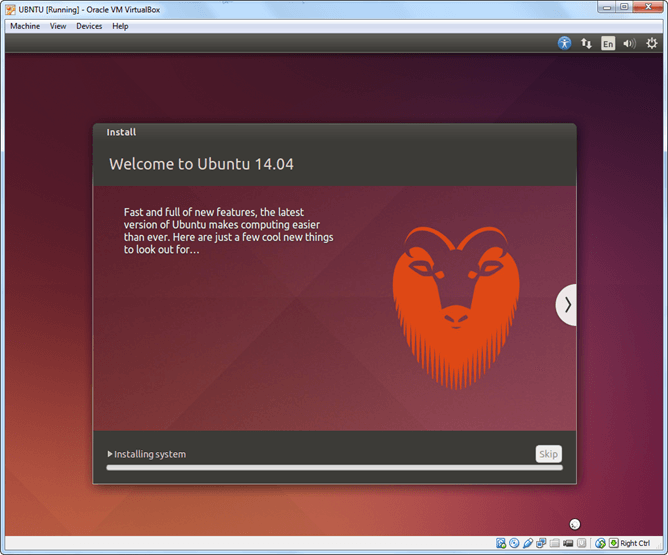
Step-11) Installation process starts. May take up to 30 minutes. Please wait until installation process completes.
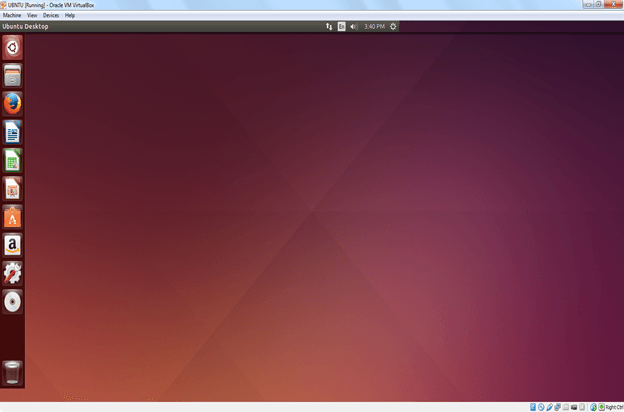
Step-12) After finishing the installation, you will see Ubuntu Desktop.
Summary
- An operating system based on the Linux kernel is called a Distribution or Distro
- There are hundreds of Distributions available, some of which are designed to accomplish a sole purpose like running servers, act as network switches, etc.
- Naming the best Linux Distribution is difficult as they are made for different.
- Linux can be installed on your system via the below-mentioned methods:
- USB stick
- Live CD
- Virtual Installation
Linux vs Windows: What’s the Difference?
It’s time to make the big switch from your Windows or Mac OS operating system.
Mac OS uses a UNIX core. Your switch from Mac OS to Linux will be relatively smooth.
It’s the Windows users who will need some adjusting. In this tutorial will introduce the Linux OS and compare it with Windows.
In this tutorial will introduce the Linux OS and compare it with Windows.
Windows Vs. Linux File System
In Microsoft Windows, files are stored in folders on different data drives like C: D: E:
But, in Linux, files are ordered in a tree structure starting with the root directory.
This root directory can be considered as the start of the file system, and it further branches out various other subdirectories. The root is denoted with a forward slash ‘/’.
A general tree file system on your UNIX may look like this.
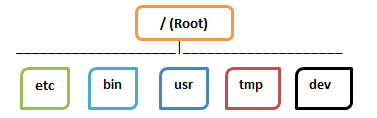
Types of Files
In Linux and UNIX, everything is a file. Directories are files, files are files, and devices like Printer, mouse, keyboard etc.are files.
Let’s look into the File types in more detail.
General Files
General Files also called as Ordinary files. They can contain image, video, program or simply text. They can be in ASCII or a Binary format. These are the most commonly used files by Linux Users.
Directory Files
These files are a warehouse for other file types. You can have a directory file within a directory (sub-directory).You can take them as ‘Folders’ found in Windows operating system.
Device Files:
In MS Windows, devices like Printers, CD-ROM, and hard drives are represented as drive letters like G: H:. In Linux, there are represented as files.For example, if the first SATA hard drive had three primary partitions, they would be named and numbered as /dev/sda1, /dev/sda2 and /dev/sda3.
Note: All device files reside in the directory /dev/
All the above file types (including devices) have permissions, which allow a user to read, edit or execute (run) them. This is a powerful Linux/Unix feature. Access restrictions can be applied for different kinds of users, by changing permissions.
Windows Vs. Linux: Users
There are 3 types of users in Linux.
- Regular
- Administrative(root)
- Service
Regular User
A regular user account is created for you when you install Ubuntu on your system. All your files and folders are stored in /home/ which is your home directory. As a regular user, you do not have access to directories of other users.
Root User
Other than your regular account another user account called root is created at the time of installation. The root account is a superuser who can access restricted files, install software and has administrative privileges. Whenever you want to install software, make changes to system files or perform any administrative task on Linux; you need to log in as a root user. Otherwise, for general tasks like playing music and browsing the internet, you can use your regular account.
Service user
Linux is widely used as a Server Operating System. Services such as Apache, Squid, email, etc. have their own individual service accounts. Having service accounts increases the security of your computer. Linux can allow or deny access to various resources depending on the service.
Note:
- You will not see service accounts in Ubuntu Desktop version.
- Regular accounts are called standard accounts in Ubuntu Desktop
In Windows, there are 4 types of user account types.
- Administrator
- Standard
- Child
- Guest
Windows Vs. Linux: File Name Convention
In Windows, you cannot have 2 files with the same name in the same folder. See below –
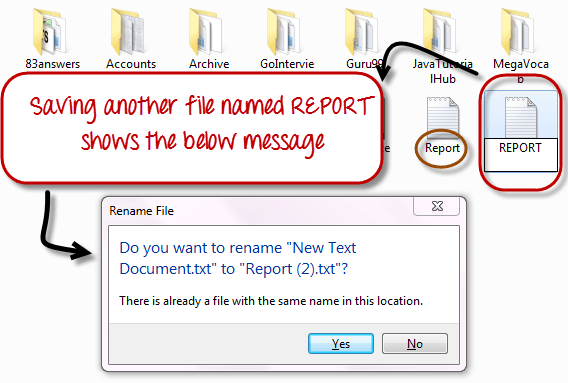
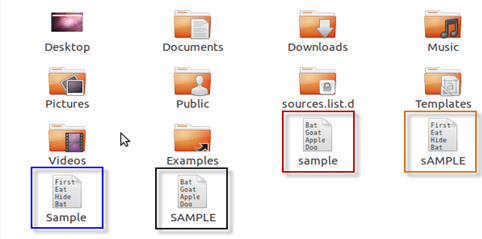
While in Linux, you can have 2 files with the same name in the same directory, provided they use different cases.
Windows Vs. Linux: HOME Directory
For every user in Linux, a directory is created as /home/
Consider, a regular user account “Tom”. He can store his personal files and directories in the directory “/home/tom”. He can’t save files outside his user directory and does not have access to directories of other users. For instance, he cannot access directory “/home/jerry” of another user account”Jerry”.
The concept is similar to C:\Documents and Settings in Windows.
When you boot the Linux operating system, your user directory (from the above example /home/tom) is the default working directory. Hence the directory “/home/tom is also called the Home directory which is a misnomer.
The working directory can be changed using some commands which we will learn later.
Windows Vs. Linux: Other Directories
In Windows, System and Program files are usually saved in C: drive. But, in Linux, you would find the system and program files in different directories. For example, the boot files are stored in the /boot directory, and program and software files can be found under /bin, device files in /dev. Below are important Linux Directories and a short description of what they contain.
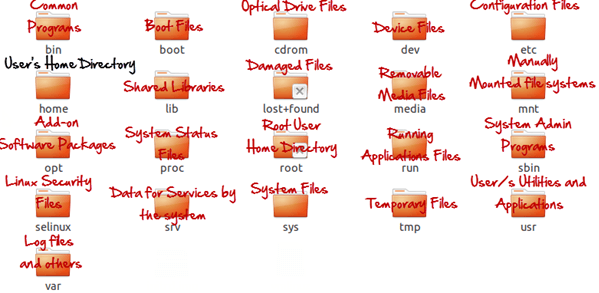
These are most striking differences between Linux and other Operating Systems. There are more variations you will observe when switching to Linux and we will discuss them as we move along in our tutorials.
Windows Vs. Linux:
| Windows | Linux |
|---|---|
| Windows uses different data drives like C: D: E to stored files and folders. | Unix/Linux uses a tree like a hierarchical file system. |
| Windows has different drives like C: D: E | There are no drives in Linux |
| Hard drives, CD-ROMs, printers are considered as devices | Peripherals like hard drives, CD-ROMs, printers are also considered files in Linux/Unix |
| There are 4 types of user account types 1) Administrator, 2) Standard, 3) Child, 4) Guest | There are 3 types of user account types 1) Regular, 2) Root and 3) Service Account |
| Administrator user has all administrative privileges of computers. | Root user is the super user and has all administrative privileges. |
| In Windows, you cannot have 2 files with the same name in the same folder | Linux file naming convention is case sensitive. Thus, sample and SAMPLE are 2 different files in Linux/Unix operating system. |
| In windows, My Documents is default home directory. | For every user /home/username directory is created which is called his home directory. |
KEY DIFFERENCE
- Linux is an open source operating system so user can change source code as per requirement whereas Windows OS is a commercial operating system so user doesn’t have access to source code.
- Linux is very well secure as it is easy to detect bugs and fix whereas Windows has a huge user base, so it becomes a target of hackers to attack windows system.
- Linux runs faster even with older hardware whereas windows are slower compared to Linux.
- Linux peripherals like hard drives, CD-ROMs, printers are considered files whereas Windows, hard drives, CD-ROMs, printers are considered as devices
- Linux files are ordered in a tree structure starting with the root directory whereas in Windows, files are stored in folders on different data drives like C: D: E:
- In Linux you can have 2 files with the same name in the same directory while in Windows, you cannot have 2 files with the same name in the same folder.
- In Linux you would find the system and program files in different directories whereas in Windows, system and program files are usually saved in C: drive.
